Dental implant surgery is a procedure that replaces tooth roots with metal, screwlike posts and replaces damaged or missing teeth with artificial teeth that look and function much like real ones. This surgical procedure offers a welcome alternative to dentures or bridgework that doesn’t fit well and can provide an option when a lack of natural teeth roots does not allow for building denture or bridgework tooth replacements. The success of dental implant surgery depends on the type of implant used and the condition of the patient’s jawbone.
Benefits of Dental Implants
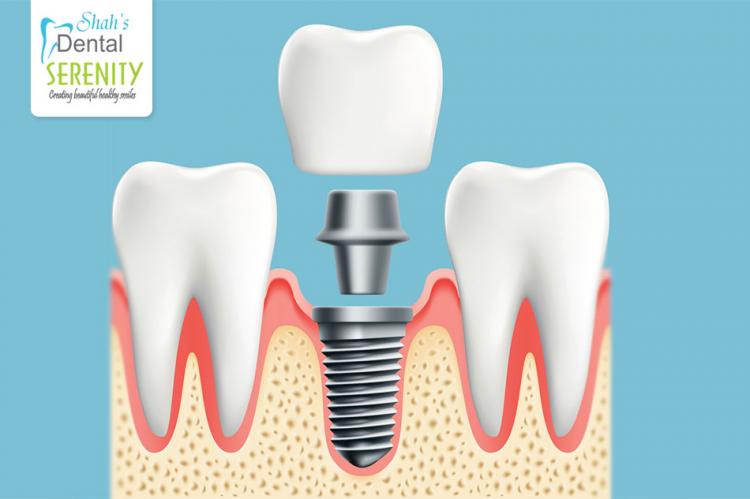
Dental implants serve as the roots of missing teeth and fuse with the jawbone, providing a stable foundation for replacement teeth. They offer several advantages over other tooth replacement options. Dental implants do not slip, make noise, or cause bone damage like fixed bridgework or dentures.
Additionally, they do not decay like natural teeth that support regular bridgework. Dental implants can improve speech, as they are securely anchored in the jawbone and feel like natural teeth. They also eliminate the need for messy adhesives to keep dentures in place. Overall, dental implants look, feel, and function like natural teeth, providing a long-lasting solution for tooth loss.
Risks and Considerations
Like any surgery, dental implant surgery comes with certain risks.
However, these risks are rare, and when problems do occur, they are usually minor and easily treatable. Some potential risks include infection at the implant site, injury or damage to surrounding structures, and nerve damage that can cause pain, numbness, or tingling. In some cases, dental implants placed in the upper jaw may protrude into one of the sinus cavities, leading to sinus problems. It’s essential for patients to thoroughly discuss these risks with their dental specialists before undergoing the procedure.
Types of Dental Implants
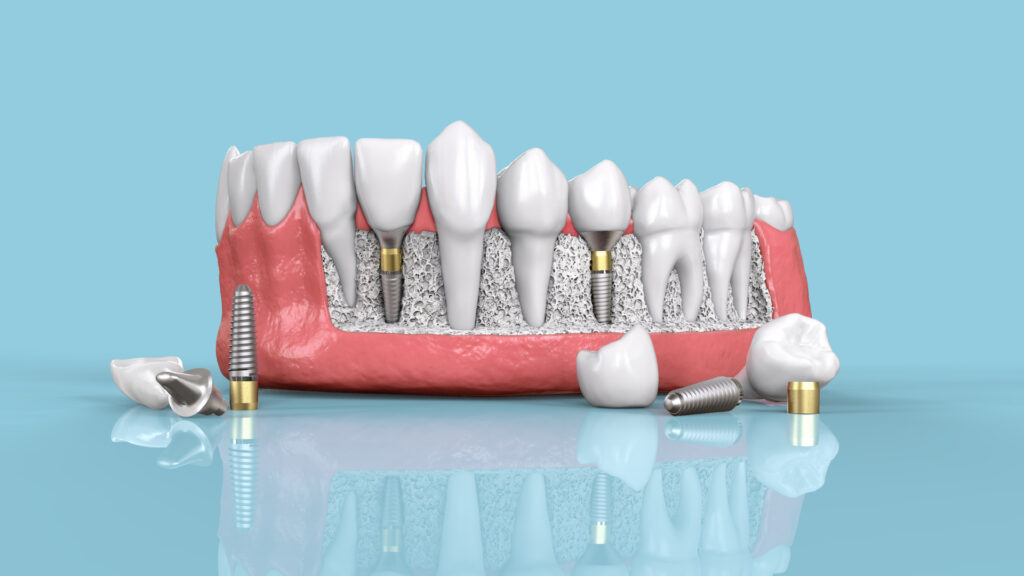
There are two primary types of dental implants: endosteal implants and subperiosteal implants. Endosteal implants are the most common type and involve placing screws, cylinders, or blades into the jawbone. Each implant holds one or more prosthetic teeth. This type of implant is often suitable for patients with existing bridges or removable dentures.
On the other hand, subperiosteal implants are placed on top of the jaw with metal framework posts that protrude through the gums to hold the implant in place. Subperiosteal implants are typically recommended for patients who cannot wear conventional dentures and lack adequate bone height to support an endosteal implant.
Candidate Criteria for Dental Implants
To be a suitable candidate for dental implants, individuals should be in good general and oral health, have adequate bone in their jaw to support the implant, and possess healthy gum tissues free of periodontal disease. The mouth’s soft tissues (gums) and underlying hard tissues (bone) play a crucial role in the success of dental implants. Patients with chronic diseases or those who smoke may have limitations or complications regarding the implant healing process.
The Dental Implant Procedure
Preparation for dental implant surgery involves a comprehensive dental exam, including X-rays, 3D images, and the review of medical history. It is necessary to evaluate bone quantity, the condition of existing teeth, and the overall health of oral tissues. Depending on the patient’s situation, a customized treatment plan is created, considering factors such as the number of teeth to be replaced and the condition of the jawbone and remaining teeth. Anesthesia options for the procedure include local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences. After surgery, patients should follow specific instructions regarding eating, drinking, and rest.
The steps of the implant placement process include damaged tooth removal, jawbone preparation (grafting if necessary), dental implant placement, bone growth and healing, abutment placement, and artificial tooth placement. This entire process can take several months to complete, with a significant portion dedicated to healing and ensuring the growth of new bone around the implant. In cases where bone grafting is required, additional time is needed for the transplanted bone to support the implant adequately. The choice between removable or fixed artificial teeth depends on individual circumstances, and patients should discuss this with their dental specialist.
Recovery and Long-Term Care
After the dental implant surgery, patients may experience swelling, bruising, minor bleeding, and pain at the implant site. Pain medications or antibiotics may be prescribed to manage discomfort and prevent infection. During the recovery period, it is advisable to eat soft foods while the surgical site heals, and stitches may require removal if they are not self-dissolving. Regular follow-up visits are essential to ensure the health and proper functioning of the implants and to receive professional cleanings. Good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, are necessary to maintain the health of implants, artificial teeth, and gum tissue.
FAQs
- What is dental implant surgery?
Dental implant surgery is a procedure that replaces tooth roots with metal posts and places artificial teeth to restore function and aesthetics. - Who is a suitable candidate for dental implant surgery?
Ideal candidates for dental implant surgery are individuals in good general and oral health, have adequate bone to support the implant, and have healthy gum tissues. - What are the potential risks and complications associated with dental implant surgery?
Potential risks of dental implant surgery include infection, injury to surrounding structures, nerve damage, and sinus problems in the upper jaw. - How long is the recovery period after dental implant surgery?
The recovery period for dental implant surgery varies based on individual healing, but it can take several months for the implant to fully integrate with the jawbone.
In summary, dental implant surgery is a reliable and effective solution for replacing missing or damaged teeth. It offers numerous benefits, including improved aesthetics, function, and durability. Understanding the procedure, risks, and recovery process is essential for individuals considering dental implants as a long-term tooth replacement option. By following proper care and maintenance protocols, patients can enjoy the benefits of dental implants for many years to come.