Dental implant surgery is a procedure that involves replacing tooth roots with metal, screw-like posts and replacing damaged or missing teeth with artificial teeth that look and function like real ones. This surgery provides a welcome alternative to dentures or bridgework that doesn’t fit well and can be a viable option for individuals who lack natural teeth roots necessary for building denture or bridge tooth replacements. The procedure varies depending on the type of implant and the condition of the jawbone, often involving multiple stages and months of healing for the bone to tightly heal around the implant.
Dental implants are surgically placed in the jawbone to serve as the roots of missing teeth. Compared to fixed bridgework or dentures, dental implants offer advantages such as stability, no slipping or noise, no bone damage, and the ability to function and decay-proof like natural teeth. Individuals who are missing one or more teeth, have a fully grown jawbone, have adequate bone to secure the implants, have healthy oral tissues, and are willing to commit to the process are potential candidates for dental implants.
However, patients with health conditions that affect bone healing, those who are unable or unwilling to wear dentures, and smokers may not be suitable candidates.
Risks and Precautions
Like any surgery, dental implant surgery carries some health risks, although they are usually minor and easily treatable. Potential risks include infection at the implant site, injury or damage to surrounding structures such as teeth or blood vessels, nerve damage causing pain or numbness, and sinus problems in cases where implants protrude into the sinus cavities. It is important to consult with a medical professional and disclose any medical conditions, medications, and orthopedic implants to evaluate the risk factors and necessary precautions.
Preparing for dental implant surgery involves a comprehensive dental exam, review of medical history, and treatment planning tailored to the individual’s situation. This may include dental X-rays, 3D images, and models of the teeth and jaw. It is essential to inform the doctor about any medical conditions and medications, as well as any heart conditions or orthopedic implants that may require antibiotics before surgery. Anesthesia options are available, including local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s specific needs. Proper eating and drinking instructions before surgery will be provided, and arrangements for post-surgery transportation should be made for sedation or general anesthesia procedures.
Surgical Procedure and Recovery
Dental implant surgery is typically performed in stages, as an outpatient procedure with healing time between each stage. The process involves several steps, including damaged tooth removal, jawbone preparation (bone grafting if necessary), dental implant placement, bone growth and healing, abutment placement, and artificial tooth placement. The entire process can take several months, with healing and waiting for the growth of new bone in the jaw.
However, specific steps can sometimes be combined depending on the situation, procedure, or materials used.
In cases where the jawbone is not thick enough or too soft to support the implant, bone grafting may be necessary to create a more solid base. This process utilizes different materials, including natural bone grafts from another location in the body or synthetic bone grafts that provide support structures for new bone growth. The amount of time required for the transplanted bone to grow enough to support a dental implant varies and may involve minor bone grafting during the implant surgery or a separate procedure depending on the condition of the jawbone.
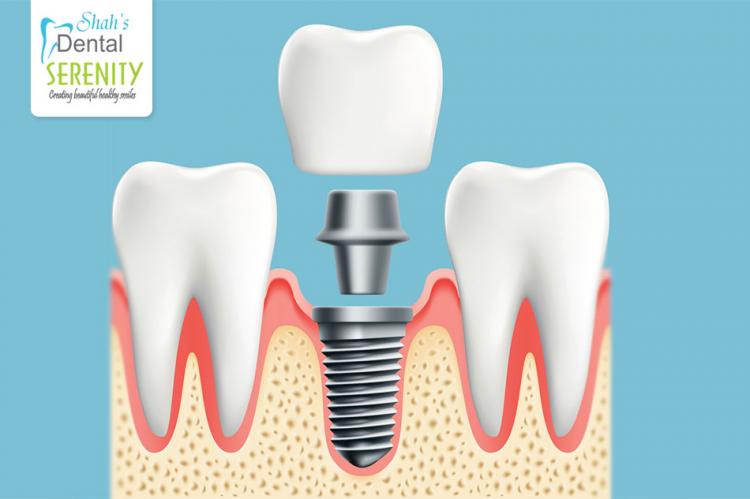
During the surgery to place the dental implant, an oral surgeon makes a cut to open the gum and expose the bone. Holes are drilled into the bone to place the dental implant metal post deep into the bone. At this stage, a temporary denture may be placed for appearance before the implant fully heals. Osseointegration, the process in which the jawbone grows into and unites with the surface of the dental implant, begins after the implant post is placed. This process helps provide a solid base for the new artificial tooth, similar to natural roots. Once osseointegration is complete, additional surgery might be required to place the abutment, the piece where the crown will be attached.
Long-term Results and Maintenance
Dental implants have a high success rate, but complications can occur. Factors that may contribute to implant failure include smoking and certain medical conditions. To ensure the longevity and proper functioning of dental implants, practicing excellent oral hygiene is crucial. Brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups are necessary to keep the implants, artificial teeth, and gum tissue clean. Specially designed brushes, such as interdental brushes, are useful for cleaning hard-to-reach areas. Avoiding damaging habits like chewing hard items and receiving treatment for teeth grinding is also important.
Regular dental checkups allow the dentist to monitor the health and proper functioning of the implants, provide professional cleanings, and address any concerns. If the implant feels loose or painful, it is important to notify the dental provider immediately. Most dental implant systems are made of materials that are evaluated according to international consensus standards for safety and biocompatibility. However, individuals with dental implants should inform healthcare providers before undergoing MRI or X-ray procedures, as dental implants can interfere with or distort these images.
FAQs
What are dental implants?
Dental implants are titanium or ceramic posts that serve as artificial teeth roots, providing a solid foundation for fixed or removable replacement teeth. They can restore the ability to chew, improve cosmetic appearance, prevent bone loss, keep adjacent teeth stable, and enhance overall quality of life.
Are dental implants suitable for everyone?
Dental implants are generally suitable for individuals with good general and oral health, a fully grown jawbone, sufficient bone to hold the implant, and healthy gum tissue. However, certain medical conditions and poor oral hygiene may make an individual ineligible for dental implants.
What is the procedure for getting dental implants?
The procedure involves stages such as tooth removal, bone grafting if necessary, implant placement, gum healing, placement of the artificial tooth connector, healing of the gums, and placement of the new tooth. The process requires several surgeries and months of healing, but it offers a comfortable and long-term solution compared to dentures.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with dental implants?
Potential risks include damage to surrounding natural teeth during implant placement, injury to surrounding tissues, inadequate function or feeling of looseness, implant body failure, difficulty cleaning around the implant, untreated periodontal disease, post-surgical numbness, and complications related to systemic or local infection. Prompt reporting of adverse events to healthcare providers and the FDA is encouraged.
In conclusion, dental implant surgery is a valuable procedure for individuals who are missing teeth and seek an alternative to traditional dentures. It provides numerous benefits, including improved chewing ability, comfort, oral health, appearance, and durability. While risks exist, they are usually minor and can be easily treated. Proper preparation, anesthesia options, post-operative care, and long-term maintenance contribute to the success and longevity of dental implants. Consultation with a dental professional is essential to assess eligibility and receive personalized advice regarding dental implant surgery.